Concept Document
Game project, a global strategy simulator of civilization development - The Great Tribes
https://www.facebook.com/groups/221419931946225/
1. Classification
Genre: global strategy, simulator.
Time of one walkthrough: 10 + hours.
Platform: PC.
2. Main Features
The Great Tribes is a global strategy simulator of civilization development, the action of which takes place in the historical period from 3000 BC to the beginning of 3000 AD. During the game the player will have to create their own unique civilization and try their hand at its development in a nonlinear, constantly changing world.
Conceptually, the game is a cross between a turn-based strategy Sid Meier’s Civilization VI and strategies of Paradox Interactive (Crusaders, Europe and Victoria). Similarity with these games is limited to the time period covered in the game and some game mechanics.
In our project we want to reflect the role of a personality in history, but instead of personalities history is influenced by different factions.
We focus on working out in detail of various historical phenomena. We are planning to create an advanced economic system that will make it possible to simulate economic processes with a high degree of realism. The simulation of interaction between different countries includes:
diplomatic relations, economic, technological, cultural and social influence.
The conduct of military actions between the countries in our project will be realized in a wide range, from single collisions to waging a trench warfare at a vast front.
Realistic simulation of the historical process
The game model is based on the results of the latest research in various scientific fields: from history and political science to geology and agricultural sciences. Simulation allows to simulate all the significant historical phenomena and processes.
Flexible Turn-based Gameplay System
The calculation of the game turn is divided into a turn and a tick.
The turn calculates global parameters: population and economy growth, migration of strata and changes in their characteristics, etc. During the game it is possible to change the time step depending on the player’s preferences.
Ticks only occur in combat. There are 4 ticks in the course of the turn:
spring, summer, autumn and winter. Thus, the army that committed a long march-throw and entered the battle running out of action points will fight in the winter tick with the corresponding consequences.
Advanced Technology System
Technological discoveries occur randomly, and the probability depends on the accumulation of a corresponding number of technological points:
agricultural, industrial, military or social. After the discovery, the technology is embedded into one or another technology package, which has an impact on a particular game system. Mechanics of technological packages allows to make development in the game realistic and not always predictable.
Two-dimensional Social System
The population in the game is grouped into strata and factions.
Strata determines the place of the household in the labour division while the factions are responsible for the redistribution of power in the game.
For example, the insufficient number of strata workers could hamper industrialization of the country and the trade union faction can fight for the rights of this small strata.
Flexible Coalition System
The coalition system allows to create various forms of relations between administrative units: an administrative zone and a region, a region and a country, between several countries (confederations, vassal relations, unions, etc.), between a region and an army (government armies, feudal armies, etc.).
Realistic Economic System
Economy in the game is a system based on the dynamic cost of resources, goods and services. This makes it possible to simulate a variety of regional specializations, economic imbalances, etc.
Unique Political System
The main elements of the political system in the game are the form of government, political values, laws and corruption. The form of government is based on the ratio of five elements: barbarism, community, democracy, oligarchy and monarchy.
Changing the ratio of these elements, it is possible to simulate any existing or even a non-existent form of government.
Political values reflect the position of the elite on each of the political or parapolitical issues. During the game the elite (of its own free will or under the pressure of the player) can change their values, but, as a rule, it is painful and not fast.
Laws allow to carry out quite a fine adjustment of the country, and corruption can help to restrain the player from excessive expansion of their power.
Diversity of Cultural and Civilization Forms
Unlike other games, civilizations in the game are formed on the basis of 4 pairs of framework principles, which can form up to 16 unique civilizations, and their combination allows to generate up to 3520 unique cultures.
Conduct of Military Operations
The military aspect of the game focuses on the strategic management of armies: formation of military doctrines, establishment of the conduct strategy of armies, determination of the optimum correlation of branches of armed forces for this or that army, etc. The player will be able to concentrate on planning the strategy of the military campaign.
3. Gameplay
The main task of the player is to develop their country in conditions of external threat and/or internal instability. By controlling a multitude of mechanisms, the player can implement any of the goals offered in the game: creation of the richest trading empire, holding power in the role of one ruling dynasty as long as possible, being the first to implement the industrial revolution, etc.
4. Game Map
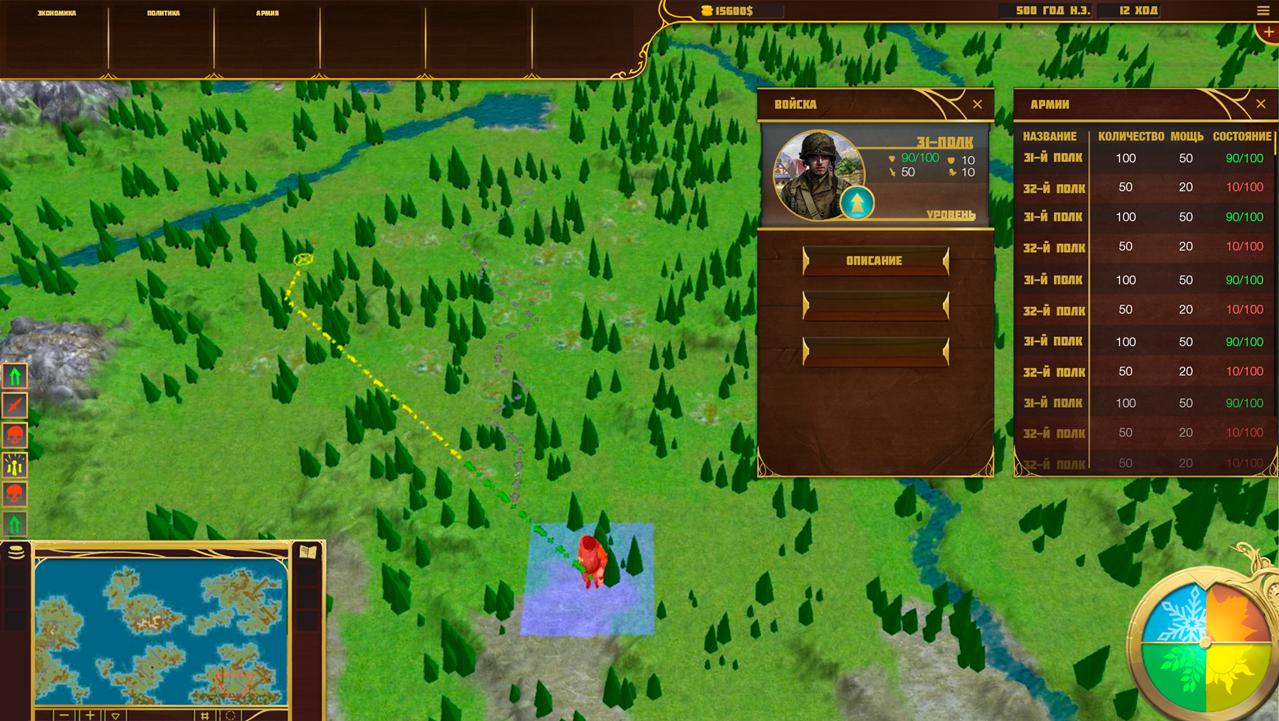
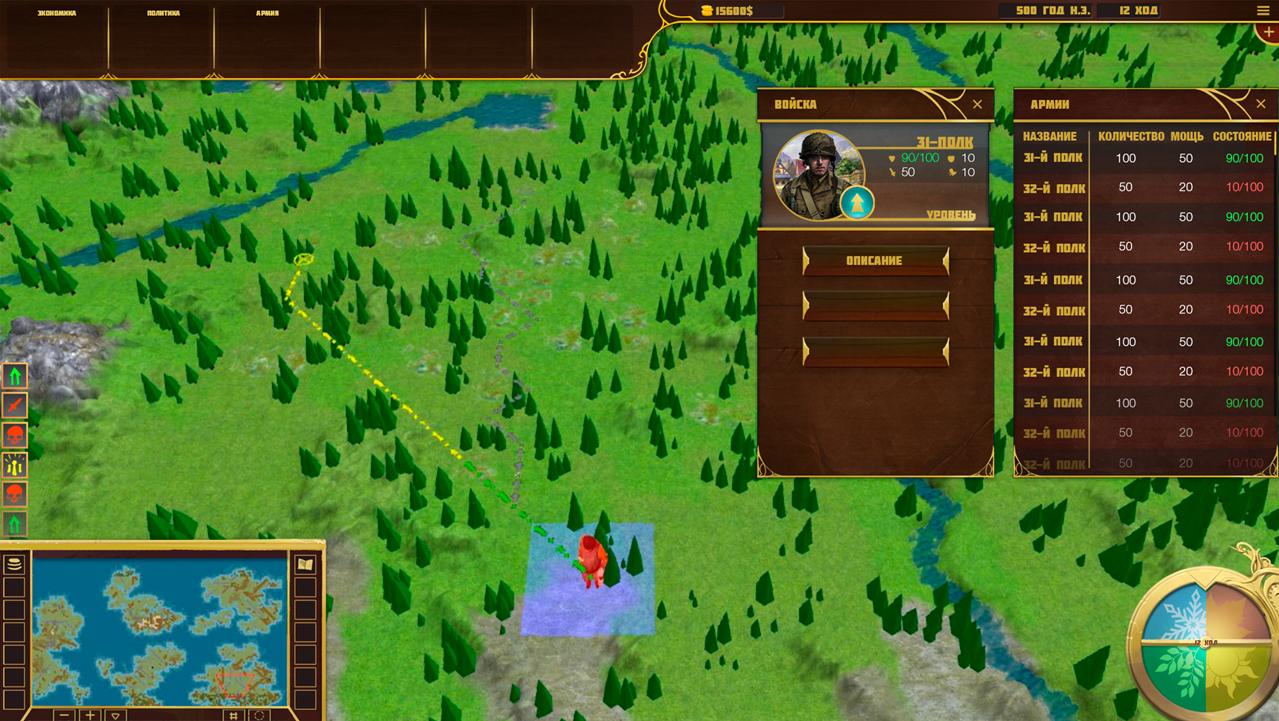
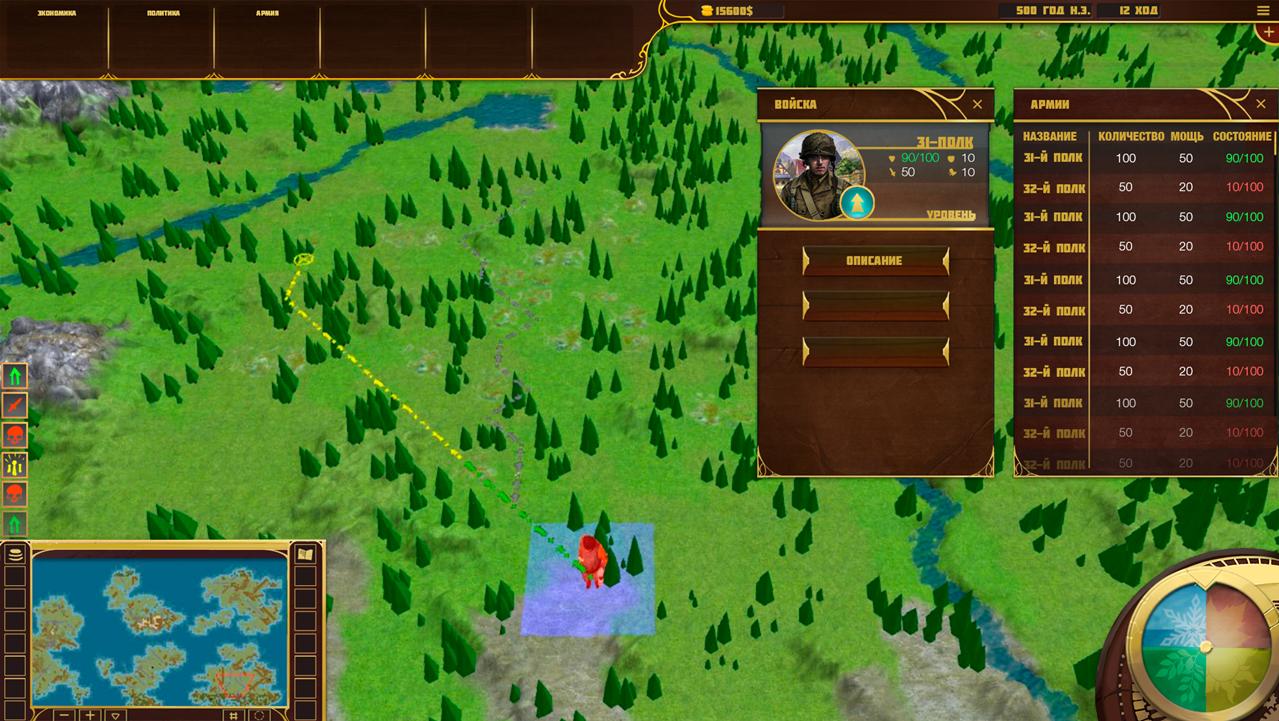
The game map is divided into tiles and subtiles. But this division is valid for the technical side of the game. In terms of gameplay, the map is divided into tiles only.
Each tile occupies an area of 1369 sq. km (this value may change during balancing). Within this area on a tile there can be located districts (in the cities), buildings (outside the settlements), the tile can be divided into different types of biomes, etc.
Depending on the biome, a certain amount of resources may be situated on the tile. So, it is advantageous to place fields on meadow plains, the area of which depends on the area of agricultural lands of the tile.
In addition, each tile has a certain level of transport infrastructure, which defines the movement speed of armies and the capacity of trade caravans.
However, unlike armies, caravans can move only along the main routes which are indicated on the map. This path can change its trajectory, depending on the quality of transport infrastructure of neighboring tiles, crime rates and other factors.
The closer is the tile to the crime center (the settlement of the player or another country or a bandit/pirate settlement), the higher is its crime rate.
On the map there constantly appear bandit armies, so they are exactly simulated by this parameter, only without the need to constantly drive armies across the country to destroy them. Rebel armies will be represented in the form of full armies.
In addition to the transport infrastructure, there is a parameter of urban infrastructure. The urban infrastructure represents the level of development of various services and engineering networks of the settlement (accessibility and quality of utilities, communication facilities, urban transport, catering, retail, emergency services, etc.). Urban infrastructure is available not only in cities but also in villages. To create favorable conditions in the settlements the player will have to balance between the development of transport and urban infrastructure.
5. Administrative division and types of settlements
The game has three levels of control: a country, region and administrative zone.
An administrative zone is a territory with dynamic boundaries, being controlled by the settlement. Within this territory, residents of the settlement can build anything within the framework of the ongoing development programme. All types of settlements without exception have this zone, from villages to cities. If a city in the region forms a new region, all the tiles in its administrative zone also become part of the new region.
Administrative zones are grouped into a larger formation – a region.
A region is a territory with dynamic boundaries, consisting of a certain number of administrative zones. It necessarily includes the capital city of the region. Unlike the administrative zone, a region can simultaneously be a country (consisting of one region). In addition, the player can directly manage it (whereas administrative zones can be managed only through legislation).
A country is the highest level of control in the game (not counting international coalitions), representing one region or a coalition of regions.
A coalition means not the country’s federal structure, but the system which defines relations between different administrative units in the game.
Each country has a capital, and as a consequence - the capital region.
The region of this type has the same functionality as a usual region, but in addition it hosts the highest state bodies: ministeries and the advisory board.
Each level of management has its own central settlement. It can be a village (only for the administrative zone), city or encampment.
A village is a type of settlement focused on food production or resource extraction. Over time a village can be upgraded into a city.
The game presents 3 basic types of villages: agricultural, resource-extracting and military.
An agricultural village is oriented to the processing of farmland.
A resource-extracting village is focused on the extraction of minerals.
The type of resources that are extracted depends on the demand for the resource.
A military village generalizes a variety of villages, the inhabitants of which are hostile to the player.
A rebel village: village troops will defend their village and their independence. A village becomes rebellious if the population’s loyalty to power is too low.
A bandit (pirates) village: village troops will attack the settlements and trade routes located nearby. A village prefers to move into this state due to absence of legal means to maintain an acceptable standard of living.
The given types of villages are conventional. All villages have the same characteristics, but their chosen vector of development depends on the demand for a particular resource, or on the level of loyalty to power.
New villages in the game can be formed either automatically or due to a certain decision. The place of automatic appearance of villages is determined on the basis of attractiveness of adjoining territories for processing, and also is located at a certain distance from other settlements and processed tiles. As the population of old settlements rises to some level, the chance of a new village emerging at some distance increases.
Its population will not appear out of nowhere, but it migrates from the settlement. New villages can occur both inside and outside the region.
Encampment is a type of settlement of nomadic cultures, able to move to other tiles. Settling, nomads form a village or city (depending on the size of the nomadic group).
Unlike a city, playing for encampment is concentrated not so much on the management of the population, but on the management of tribal clans (factions).
Each clan has its own encampment. The elite of each nomadic group includes every member of the clan. However, the encampment can include residents who are not part of the clan (slaves, mercenaries, etc.). The more solid (controlled) the clans are, the stronger the tribe is in clashes with other nations. This clan structure of the society is typical of all countries with barbaric elements of government. However, in settled states clans do not always act as the elite of the settlement.
In addition, unlike cities, change of dominant elites in the tribe occurs not gradually through transfer of population from one faction to another, but via change of the fraction status. In game mechanics it is represented in the form of change of the capital nomads and status of the elite.
Another distinguishing feature of nomads is their ability to move around the map. This is possible in two ways:
- moving the nomadic population of the ruling clan, while the rest of the nomads are moved in automatic mode (due to an insufficient level of control or by the decision of the player);
- moving all the nomads manually with a sufficient level of control.
Poorly controlled nomads are moved in automatic mode.
A city is a type of settlement with multiple forms of activity, but with a certain specialization. A city is not necessarily a result of the village development, but it can be built from scratch, or formed from the outpost (see Regional buildings). Unlike a village or encampment, a city that is the capital of a region or country can have up to three Wonders of the world (one of each level: regional, national and international).
In the game there are many specializations of cities:
- Administrative center
- Science center
- Trade center
- Cultural center
- Religious center
- Industrial city
The higher the city is placed in the hierarchy (a provincial city - the capital of the region - the capital of the country), the greater effect its specialization produces. So, if the player decided to build a huge empire, it is better to establish an administrative center as the capital (for the control of large territories), for a trading empire it should be a trade center, and for theocracy it is more preferable to assign a religious center of a state religion, etc.
The difference between a city and a village: a city has a more developed social infrastructure; it occupies a certain area of the tile and when it is exceeded, it expands to a neighboring tile; a city creates an administrative load; it is possible to construct wonders of the world (in capitals); it has diverse stratification and division into districts.
6. Urban districts
In the city, a player can build up to seven districts that can be expanded to accommodate various infrastructures:
An administrative district performs functions of control and development of the administrative resource;
An industrial district produces practically all types of goods (except luxury);
A cultural district produces luxury goods, prestige, and also creates some modifiers for the city;
A scientific district is responsible for increasing literacy of the population and accelerating the development of technologies;
A religious district - the development of the district contributes to increasing the influence of state religion;
A commercial district – transport and financial infrastructure is created here;
A social district provides the population with housing and urban infrastructure.
Six of the listed districts can be built in the city center and determine its specifics.
In addition, the effect of all districts depends on the location of the city – it can be situated near the shore or in the depths of the continent.
Characteristics of districts
Cost includes resources needed for the region expansion.
Content includes resources necessary for supply of the district during each turn.
Workforce is the number of working hands required for the efficient operation of the district.
Area is the area given and available for expansion.
Effect stands for the bonus-malus payments, received in the course of functioning of the district.
Wonders of the World
Instead of usual constructions three types of wonders of the world are built in cities: regional, national and global. The effect of every kind of wonders is spread according to their scale.
The list of wonders available for construction in the city depends on the central district of the city. And the effect produced by the district will be determined by the chosen wonder. In addition, the district can include up to three wonders, one of each level.However, construction of a higher-level wonder reduces the effect of wonders of a lower level. The wonder effect can also be reduced by the presence of a similar wonder in the zone of influence and visibility.
The scale of the wonder influences its price and effect. In addition, the effect of a small wonder can easily disappear if certain conditions are not fulfilled, whereas the effect of a world wonder never disappears.
7. Regional buildings
In addition to the wonders of the world and urban districts, the player can also build constructions outside the city - in regional and extraregional tiles.
Characteristics of regional buildings:
Cost stands for resources necessary for construction.
Supply includes resources necessary for ensuring the construction during each turn.
Workforce is the number of working hands required for an efficient operation of a building.
Location defines whether it is possible to build a construction only within the district or everywhere.
Improvement - some buildings can be rebuilt into other more significant constructions.
For example, a wooden advance outpost can be upgraded into a stone one.
Accommodation conditions - most buildings can be built only in tiles with certain conditions.
Effect - buildings can produce a variety of effects: from ordinary bonuses to the ability to extract resources and supply armies.
List of buildings
Agricultural: gardens, a pasture, a field, a camp;
Mining: a quarry, a sawmill, a mine, a drilling rig;
Military: an outpost, a military base.
Unlike other buildings, outposts can be installed outside the district.
The outpost has its own control zone, which complicates the speed of enemy forces passing through it, and decreases the level of crime in the district.
In addition, outposts with a sufficiently high level of development of urban infrastructure can be converted into a city or village.
8. Domestic Policy
The key indicators of domestic policy are the administrative burden and the administrative resource.
The administrative burden is the level of constant administrative spendings on the management of the country, as well as various actions of the player.
The administrative burden of the country is the burden of the regions and the highest governmental structures.
The administrative resource is the management resource which represents the number of civil cervants and their management efficiency. If the administrative load exceeds the administrative resource, the player begins to lose control over the regions.
In addition, the administrative resource can be spent on corrupt practices.
Corruption in the game is trade in administrative resource, carried out by the management apparatus. Like for any resource, the laws of supply and demand apply to the administrative resource. Strata that captured part of the administrative resource of the city, region or country get the opportunity to determine the actions of a chosen government institution.
In addition to trade in the administrative resource, corruption is expressed in the form of an indicator of the region or government structures which determines the efficiency of budget spendings on their needs.
Forms of Government
Another important element of domestic policy is the form of government.
It is a mixture of five elements: barbarism, community, democracy, oligarchy and monarchy. Each element can take a value from 0 to 10, where 0 is the absence of characteristics and 10 is its pure, pronounced characteristics. For example, a country may have the following form of government: barbarism (5), community (3) and oligarchy (2).
Total expressiveness of all forms of government should be equal to 10, so to increase an element, for example, democracy one must reduce the strength of one of the remaining elements.
Each of the elements of the form of government gives its own unique effect and when changing the form of rule the gameplay changes accordingly.
Forms of government also give access to
- certain social technologies.
Some of the technologies are closed from some forms of government.
For example, rooted barbarism closes access to tax collection and trade technologies. - to the laws
For example, a strong monarchy gives an opportunity to pass a law on inheritance of power.
Political values
Political values reflect the standpoint of the strata and factions on each of the political or parapolitical issues. In the course of the game they (of their own will or under the player’s pressure) can change their values, but, as a rule, it is painful and not fast.
The game has the following groups of values:
Economy:
a hard plan \ a soft plan \ pragmatism \ a regulated market \ a free market
Openness of the society:
closed \ moderately closed \ semi \ moderately open \ open
Social Policy:
state / state-society / society / society - individual \ individual
Foreign Policy:
isolationism \ non-interference\ realism \ interventionism \ expansionism
Religious Policy:
theocracy \ clericalism \ secularism \ anticlericalism \ militant atheism
National Policy:
n_azism \ nationalism \ multiculturalism \ internationalism \ cospomolitism
Post-values:
denied \ invalid \ neutral \ minor \ important
Post-values in the game reflect the attitude of people to the values of new, upcoming phases of development. For example, in the course of society’s transition to the industrial phase of development, issues of emancipation of women, ecology and others became significant.
The more loyal the society is to post-values, the more inclined it is to revise its other values, which can lead to social instability.
The forms of government along with the political values of the elite allow to simulate all the basic forms of political formations.
Laws
If the forms of government tell us who rules the country, then the laws show how the country is ruled. Laws can be adopted both for the whole country and for each region separately.
The adoption of any law entails a temporary decrease in the loyalty of regions. Besides, the laws are not just effects, but also constant expenses on their maintenance. The lack of resources for the maintenance of laws leads to the fact that laws cease to operate, starting from the recently introduced and ending with the most entrenched.
Forms of struggle for power
Finally, the domestic policy is expressed in the struggle for power.
Depending on the prevailing contradictions between the authorities and the opposition, the latter may make various steps to change the current power:
- Change of the party of power (occurs in the form of cabinet struggle within the established norms)
- Civil disobedience
- Insurrection / Coup d’état
- Terrorism
- Civil war
- Guerrilla war
- Participants of the guerilla movement are the strata with the state religion and culture
- Peasant War
The lower the position on the list is, the higher is the massiveness, the number of victims and the cruelty of speeches; the current rules and regulations are followed less and the speed of the process is higher, but, in case of success of the action, reforms conducted by the new power are more radical.
9. Foreign Policy
Diplomacy and Prestige
The basis of diplomatic relations in the game is the system of coalitions.
Coalition agreements can be concluded between countries, between regions and even between the capital of the region and the settlements belonging to it. In fact, it is a universal pattern of establishing communication between administrative entities.
The main resource of diplomacy is prestige. Prestige is a generalized measure of grandeur of an international organization, country, region or settlement.
This parameter affects both the other administrative entities and the perception of any entity by the population. So, a city, producing a lot of prestige, can get a good income from tourism. And a country with high prestige can tempt other countries and regions over to its side.
Espionage
Espionage in the game is an agent network that is introduced into a particular region.
The more developed the agent network is, the higher the chance of success of espionage actions or counteraction of foreign secret services is.